Best practices for machine-learned force fields: Difference between revisions
(→Basics) |
No edit summary |
||
| (92 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Using the [[:Category:Machine-learned force fields|machine- | Using the [[:Category:Machine-learned force fields|machine-learning-force-fields method]], VASP can construct force fields based on ab-initio simulations. When constructing, testing, re-learning, and applying a force field, many aspects must be carefully considered. Some best practices are listed here, but note that the list is not exhaustive and the method has not yet been applied to a large number of systems. We, therefore, recommend the usual rigorous monitoring that is necessary for all research projects. The basic steps required for machine learning force field (MLFF) training can be found on the [[Machine learning force field calculations: Basics|Basics page]] on machine learning force field calculations. | ||
== | == Training == | ||
=== Best practice training modes=== | |||
To start a training run, set {{TAG|ML_MODE}} = <tt>TRAIN</tt>. Depending on the existence of a valid {{FILE|ML_AB}} in the folder where {{VASP}} is executed, one of the two modes is automatically selected: | |||
*No {{FILE|ML_AB}} file: the training algorithm will start from zero. | |||
*{{{FILE|ML_AB}}} file is present: Training will continue based on an existing structure database. In this mode of operation, a force field is generated from the existing database ({{FILE|ML_AB}} file) and then a MD run is continued from the specified {{FILE|POSCAR}} file. This mode is used to select additional structures from the phase space of the material. But it can also be used to examine surfaces by first training the bulk material, then adding a molecule to the surface in the {{FILE|POSCAR}} file and continuing the training. | |||
If there are several atoms of the same species which should be treated differently by the machine-learning algorithm it is important to give different names to them in the {{FILE|POSCAR}} file. For example if there are oxygen atoms in a bulk material and in a molecule at the surface it is advisable to make two groups of oxygen atoms in the {{FILE|POSCAR}} and call one group O1 and and the second O2. | |||
{{NB|warning|It is not possible to give the same name to different groups of atoms in the {{FILE|POSCAR}} file and the names are restricted to two characters.}} | |||
: | |||
The training mode requires {{VASP}} to perform ab-initio calculations, so the first step is to set up the [[:Category:Electronic minimization|electronic minimization]] scheme. | |||
: | {{NB|warning|It is very important to '''not''' change the ab-initio settings in the {{FILE|INCAR}} file between training from scratch and continuing training. Likewise, the {{FILE|POTCAR}} file is '''not''' allowed to be changed when resuming training.}} | ||
* | ''' Ab-initio calculation setup ''' | ||
{{ | In general, everything that applies to {{VASP}} DFT calculations also applies here. The guidelines for [[:Category:Electronic minimization|electronic minimization]] can be used to set up the ab-initio part for on-the-fly training. | ||
Additionally, we strongly advise following these guidelines for ab-initio computation during on-the-fly learning: | |||
*Do not set {{TAG|MAXMIX}}>0 when using force fields for machine learning. During machine learning, first-principles calculations are often bypassed for hundreds or even thousands of ion steps, and ions can move significantly between first-principles calculations. In these cases, the use of {{TAG|MAXMIX}} very often results in non-converged electronic structures or errors during the self-consistency cycle. | |||
* It is generally possible to train force fields on a smaller unit cell and then apply them to a larger system. Be sure to choose a large enough structure so that the phonons or collective oscillations "fit" into the supercell. | |||
* It is important to learn the exact forces. To do this, the electronic minimization has to be checked for convergence. These checks may include, for example, the number of k-points in the {{FILE|KPOINTS}} file, the plane wave limit ({{TAG|ENCUT}}), the electronic minimization algorithm, etc. | |||
* Turn off symmetry as for standard molecular dynamics runs ({{TAG|ISYM}}=0). | |||
* For simulations without a fixed grid (NpT), the cutoff for plane waves {{TAG|ENCUT}} must be set at least 30 percent higher than for fixed volume calculations. Also, it is good to restart frequently ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=TRAIN with existing {{FILE|ML_AB}} file in working directory) to reinitialize the [[Projector-augmented-wave formalism|PAW]] basis of KS orbitals and avoid [[Energy vs volume Volume relaxations and Pulay stress#Pulay stress|Pulay stress]]. | |||
''' Molecular dynamics setup ''' | |||
== | After the forces are obtained from electronic minimization by the [[Hellmann-Feynman forces|Hellmann-Feynman Theorem]], {{VASP}} must propagate the ions to obtain a new configuration in phase space. For the molecular dynamics part, familiarity with setting up {{TAG|molecular dynamics}} runs is beneficial. In addition, we recommend the following settings in the molecular dynamics part: | ||
*Decrease the integration step ({{TAG|POTIM}}) if the system contains light elements, or increase the light element mass ({{TAG|POMASS}}) in the {{FILE|INCAR}} or the {{FILE|POTCAR}} file. As a rule of thumb, the time step should not exceed 0.7 fs and 1.5 fs for hydrogen and oxygen-containing compounds, respectively. However, a time step of 3 fs may work well for heavy elements (Si). | |||
* If possible, heat the system gradually using the temperature ramp (set {{TAG|TEEND}} higher than {{TAG|TEBEG}}). Start with a low temperature (not zero) and increase it to a temperature about 30% above the desired application temperature. This will help "on-the-fly" training to explore a larger portion of the phase space and will result in more stable force fields. | |||
* If possible, prefer molecular dynamics training runs in the [[NpT ensemble]] ({{TAG|ISIF}}=3). The additional cell fluctuations improve the robustness of the resulting force field. However, for fluids, only volume changes of the supercell are allowed, otherwise, the cell may "collapse", i.e., it tilts extremely so that the system becomes a layer of atoms. This can be achieved with {{FILE|ICONST}}, [[ICONST#Settings for item(i)|here]] and [[ICONST#Settings for status|here]]. For an example input for constraining the cell shape, see the [[ICONST#Constraints_for_volume_and.2For_the_shape_of_simulation_cell|ICONST]] page or the [[Best practices for machine-learned force fields#Example|end of this page]] page. The [[NVT ensemble]] ({{TAG|ISIF}}=2) is also acceptable for training, but use the [[Langevin thermostat]] as it is very good for phase space sampling (ergodicity) due to its stochastic nature. | |||
* One should always try to explore as much of the phase space of the material as possible. Therefore, one should always '''avoid''' training in the [[NVE ensemble|NVE]] ensemble. | |||
''' General settings for on the fly training ''' | |||
The {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=TRAIN sets already widely used default values | |||
for on-the-fly training in machine learning. Nevertheless, we | |||
would like to provide the following guidelines for setting individual machine-learning parameters: | |||
* | * If the system contains different components, first train them separately. For example, if the system consists of a crystal surface and a molecule that binds to that surface. Train the main crystal first, then the surface, possibly the isolated molecule, and finally the entire system (if you do not need to describe the isolated molecule, you can skip training for the molecule). In this way, a considerable number of ab-initio calculations can be avoided in the most computationally intensive combined system. | ||
* If you train a system containing a surface or isolated molecules do not train the stresses. For that set {{TAG|ML_WTSIF}} to a very small value in the {{FILE|INCAR}} file (e.g. {{TAG|ML_WTSIF}}=1E-10). In surface calculations, the surface is terminated by a vacuum layer which does not exert stress onto the cell. Isolated molecules are similar since they are vacuum terminated in all directions. Hence, these simulations have to be done in the NVT or NVE ensemble. | |||
* If there are not enough reference configurations taken during training (seen in {{FILE|ML_ABN}}), adjusting the default value of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}=0.02 to a lower value is advisable. The value of this flag is highly dependent on the system under consideration, so it is encouraged to determine the correct value of this flag by trial and error. | |||
* A force field is only ever applicable to the phases of the material in which it has been trained. Therefore, machine-learned force fields cannot be expected to provide reliable results for conditions for which training data have not been collected. | |||
* If | |||
* | |||
=== Retraining === | === Retraining with re-selection of local reference configurations === | ||
This mode is selected with {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=SELECT. In this mode, a new machine-learned force field is generated from the ab-initio data provided in the {{FILE|ML_AB}} file. The structures are read in and processed sequentially as if they had been obtained through an MD simulation. In other words, the same steps are performed as in on-the-fly training, but the data source is not an MD run, but the structures available in the {{FILE|ML_AB}} file. This mode of operation can be used to generate VASP force fields for machine learning from precomputed or external ab-initio datasets. The main difference with {{TAG|ML_ISTART}} = REFIT is that the list of local reference configurations in the {{FILE|ML_AB}} file is ignored and a new set is created. The newly updated set is written to the final file {{FILE|ML_ABN}}. If the calculations for {{TAG|ML_MODE}} = SELECT are too time-consuming with the default settings, it is useful to increase {{TAG|ML_MCONF_NEW}} to values around 10-16 and set {{TAG|ML_CDOUB}} = 4. This often speeds up calculations by a factor of 2-4. | |||
The automatic update of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} is not very stable at the beginning of the reselection if the force fields are not sampled sufficiently and are therefore inaccurate. Then a too-high value for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} may be determined and in all later steps the errors of the predicted forces would be below {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. Therefore, no training would be performed. To address this, {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''SELECT'' does not apply any update for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} by default ({{TAG| ML_ICRITERIA}} = 0). Also, it can be beneficial to vary {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} until a satisfactory number of local reference configurations is found (i.e. until the matching errors stop decreasing as the number of local reference configurations increases). The number of local reference configurations increases as {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} becomes smaller. It is strongly recommended to perform a more accurate SVD-based refitting afterward. | |||
=== Retraining with hyper-parameter optimization=== | |||
After you have collected a sufficient number of local atomic reference configurations, as described in Training from scratch and Continuation training, it is recommended to | |||
optimize the parameters for your force field. This will result in | |||
lower training and test set errors. The reference configurations selected in the {{FILE|ML_AB}} will not be updated. To perform a hyperparameter search, {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=REFIT must be set in the {{FILE|INCAR}} file and a {{FILE|ML_AB}} must exist in the working directory. By setting {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=REFIT, {{VASP}} automatically selects {{TAG|ML_IALGO_LINREG}}=4, which performs a regularized SVD to find the appropriate weights <math> \mathbf{w} </math> (see [[Machine Learning Force Field: Theory#Matrix Vector Shape of Linear Equations|here]] for the definition). It is favorable to enter refit mode and tune the hyperparameters to improve the fitting error, which can be found in the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} under the description '''ERR'''. To tune the hyperparameters, set the desired parameter in the {{FILE|INCAR}} file, then run {{VASP}} and check the error in the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}}. For more information on extracting errors from the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}}, see [[Best Practices for Machine-Learning Force Fields#Monitoring|here]]. Adjusting the following parameters may improve the quality of the force-fields: | |||
* Adjusting the cutoff radius for the angular and radial descriptor by adjusting {{TAG|ML_RCUT2}} and {{TAG|ML_RCUT1}}. | |||
* Matching the number of radial and angular basis functions with {{TAG|ML_MRB1}} and {{TAG|ML_MRB2}}. | |||
*The parameter {{TAG|ML_LMAX2}} should be optimized to obtain the maximum angular quantum number for spherical harmonics. | |||
*The regularization parameter for the SVD can be adjusted by setting {{TAG|ML_SIGW0}} in the {{FILE|INCAR}}. The regularization should always be set as large as possible so that the force field can be applied to structures outside of the training set. | |||
*{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}} should be used to sparsify the local reference configurations used from the {{FILE|ML_AB}}. This can improve the performance of the trained force field. However, it may also reduce the accuracy. | |||
{{NB|mind| Hyperparameter optimization should always be started from default values}} | |||
{{NB|mind| For fluids, reducing to {{TAG|ML_LMAX2}}{{=}}2 and {{TAG|ML_RCUT2}}{{=}}4 can lead to better fitting results.}} | |||
=== Accuracy === | === Accuracy === | ||
The | The achievable accuracy of the force fields depends on many factors, e.g. species, temperature, pressure, electronic convergence, machine learning method, etc. | ||
In our implementation of | In our implementation of kernel ridge regression, the accuracy of the force fields increases as the number of local reference configurations increases. This increase is not linear and at the same time, the computational cost increases linearly. When generating machine-learning force fields there is always a tradeoff between accuracy and efficiency. | ||
Here are some empirical guidelines: | Here are some empirical guidelines: | ||
* For a given structure the error increases with increasing temperature and pressure. | * For a given structure, the error increases with increasing temperature and pressure. Therefore, the force field should not be trained under conditions too far from the target condition. For example, for a production run at 300 K, it is good to learn above this temperature (450-500 K) to capture more structures that might occur in the production run, but it is not beneficial to learn the same phase at, say, 1000 K, as this is likely to reduce the accuracy of the force field. | ||
* Liquids | * Liquids typically require many more training structures and local reference configurations to achieve similar accuracy to solids. To achieve errors of about 30 meV/angstrom, liquids often require 2000-4000 local reference configurations, while 500-1000 reference configurations might be sufficient for simple periodic volume systems. | ||
* | * Typically, the fitting errors should be less than 1 meV/atom for the energies and 30-100 meV/angstrom for the forces at temperatures between 300-1000 K. Errors slightly above these values may be acceptable, but these calculations should be thoroughly checked for accuracy. | ||
=== Accurate force fields === | === Accurate force fields === | ||
The default parameters | The default parameters that control learning and sampling are chosen to provide a good tradeoff between accuracy and efficiency. In particular, the default setting for {{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}} tends to remove local reference configurations during the sparsification step, limiting accuracy. However, further decreasing {{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}} to values below 1.0E-11 does not improve accuracy, since the condition number of the regularized normal equation solved in Bayesian regression is approximately proportional to the square of the condition number of the Gram matrix considered during sparsification (see [[Machine learning force field: Theory#Sparsification of local reference configurations|here]]). Thus, if the Gram matrix has a condition number of 1E9, then the normal equation has a condition number of 1E18, which means that a loss of significance occurs when the normal equation is solved. | ||
To obtain highly accurate force fields that retain more local reference configurations, one | To obtain highly accurate force fields that retain more local reference configurations, one must use the following two-step procedure: | ||
First, | First, one performs a full on-the-fly learning: | ||
{{TAGBL|ML_IALGO_LINREG}}=1; {{TAGBL|ML_SION1}}=0.3; {{TAGBL| | {{TAGBL|ML_IALGO_LINREG}}=1; {{TAGBL|ML_SION1}}=0.3; {{TAGBL|ML_MRB2}}=12 | ||
This can consist of many different training steps | This can consist of many different training steps that include all the desired structures. Increasing {{TAG|ML_MRB1}} from 8 to 12 and decreasing {{TAG|ML_SION1}} from 0.5 to 0.3 improves the condition number of the Gram matrix by about a factor of 10 and allows the sparsification step to retain more local reference configurations (typically by about a factor of 2). Of course, this slows down the force field calculations somewhat. | ||
If full retraining is not possible, you can also try to increase only the number of local reference calculations, as described above, by using {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''SELECT'' and choosing a value for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} that gives a satisfactory number of local reference configurations. | |||
Second, readjust the force field using {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''REFIT''. | |||
Using SVD instead of solving the regularized normal equation avoids squaring the problem, and therefore the condition number of the design matrix rather than its square is important. In our experience, SVD refinement with the default value {{TAG|ML_SION1}}=0.5 always improves the accuracy of the force field. | |||
=== Monitoring === | === Tuning on-the-fly parameters === | ||
In case too many or too few training structures and local reference configurations are selected some on-the-fly parameters can be tuned (for an overview of the learning and threshold algorithms we may refer [[Machine learning force field calculations: Basics#Important algorithms|here]]): | |||
* {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}: Defines the learning threshold for the Bayesian error of the forces for each atom. In a continuation run, it can be set to the last value of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} of the previous run. This way unnecessary sampling at the beginning of the calculation can be skipped. However, when going from one structure to the other, this tag should be very carefully set. {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} is species and system dependent. Low symmetry structures, for example, liquids, have usually a much higher error than high symmetry solids for the same compound. If a liquid is learned first and the last {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} from the liquid is used for the corresponding solid, this {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} is way too large for the solid and all predicted errors will be below the threshold. Hence no learning will be done on the solid. In this case, it is better to start with the default value for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. Typical attainable values for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} are 0.02 around 300-500 K, and 0.06 around 1000-2000 K, so temperature but also system dependent. | |||
* {{TAG|ML_CX}}: It is involved in the calculation of the threshold, {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} = (average of the stored Bayesian errors in the history) *(1.0 + {{TAG|ML_CX}}). This tag affects the frequency of selection of training structures and local reference configurations. Positive values of {{TAG|ML_CX}} result in a less frequent sampling (and hence less ab-initio calculations) and negative values result in the opposite. Typical values of {{TAG|ML_CX}} are between -0.3 and 0. For training runs using heating, the default usually results in very well-balanced machine-learned force fields. When the training is performed at a fixed temperature, it is often desirable to decrease to {{TAG|ML_CX}}=-0.1, to increase the number of first principle calculations, and thus the size of the training set (the default can result in too few training data). | |||
* {{TAG|ML_MHIS}}: Sets the number of previous Bayesian errors (from learning steps for the default of {{TAG|ML_ICRITERIA}}) that are used for the update of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. If, after the initial phase, strong variations of the Bayesian errors between updates of the threshold appear and the threshold also changes strongly after each update, the default of 10 for this tag can be lowered. | |||
* {{TAG|ML_SCLC_CTIFOR}}: Scales {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} only in the selection of local reference configurations. In contrast, to {{TAG|ML_CX}} this tag does not affect the frequency of sampling (ab-initio calculations). Smaller values mean more local reference configurations are selected; large values mean fewer local reference configurations are selected. | |||
* {{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}}: Controls the sparsification of the number of local reference configurations after they were selected by the Bayesian error estimation. Increasing {{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}} increases the number of local reference configurations that are removed and by decreasing the opposite happens. This tag will also not affect the learning frequency since the sparsification is only done after the local reference configurations were selected for a new structure. We do not recommend increasing the threshold to values larger than 1E-7. Below that value this tag works well to control the number of local reference configurations, however, for multi-component systems, the sparsification algorithm tends to lead to strong imbalances in the number of local reference configurations for different species. | |||
* {{TAG|ML_LBASIS_DISCARD}}: Controls, whether the calculation continues or stops after the maximum number of local reference configurations {{FILE|ML_MB}} for any species is reached. Previously the default behavior was {{TAG|ML_LBASIS_DISCARD}}=.FALSE.: the calculation stops and requests an increase of {{FILE|ML_MB}} if the number of local reference configurations for any species reaches {{FILE|ML_MB}}. In multi-component systems, the sparse representation for one species exceeds {{FILE|ML_MB}} very quickly, while the other species are not sufficiently well described by the yet determined local reference configurations and are still far below the limit {{FILE|ML_MB}}. The present default is hence {{TAG|ML_LBASIS_DISCARD}}=.TRUE.: In this case, the code disposes of local reference configurations whenever the threshold is reached. It does this species dependent. | |||
=== Monitoring on-the-fly learning === | |||
The monitoring of your learning can be divided into two parts: | The monitoring of your learning can be divided into two parts: | ||
* Molecular dynamics/ensemble-related quantities: | * Molecular dynamics/ensemble-related quantities: | ||
** Monitor your structure visually. This means | ** Monitor your structure visually. This means looking at the {{FILE|CONTCAR}} or {{FILE|XDATCAR}} files with structure/trajectory viewers. Many times when something goes wrong it can be immediately traced back to unwanted or unphysical deformations. | ||
** Volume and lattice parameters in the {{FILE|OUTCAR}} and {{FILE|CONTCAR}} files. It is important to confirm that the average volume stays in the desired region. A strong change of the average volume over time in constant temperature and pressure runs indicates phase transitions or non-properly equilibrated systems. | ** Volume and lattice parameters in the {{FILE|OUTCAR}}, {{FILE|XDATCAR}} and {{FILE|CONTCAR}} files. It is important to confirm that the average volume stays in the desired region. A strong change of the average volume over time in constant temperature and pressure runs indicates phase transitions or non-properly equilibrated systems. Particularly troublesome is a strong shearing during a single VASP run: since VASP keeps the plane wave basis set fixed and originally uses a spherical cutoff sphere, the cutoff sphere effectively becomes an ellipsoid. That is, the effective cutoff becomes small in some reciprocal lattice directions. Lattice vector changes of more than 10 % during a single run must be avoided. The corresponding data files ( {{FILE|ML_AB}}) are not suitable to continue the training (perform your calculations in small "junks"). | ||
** Temperature and pressure in the {{FILE|OUTCAR}} and {{FILE|OSZICAR}} files. Strong deviations of temperature and pressure to the desired ones at the beginning of the calculation indicate non-properly equilibrated | ** Temperature and pressure in the {{FILE|OUTCAR}} and {{FILE|OSZICAR}} files. Strong deviations of temperature and pressure to the desired ones at the beginning of the calculation indicate non-properly equilibrated starting positions. If the desired charasteristics undergo strong oscillations optionally block averages can be used to monitor them (for more on block averages please see below under "Application"). | ||
** Pair-correlation functions ({{FILE|PCDAT}}). | ** Pair-correlation functions ({{FILE|PCDAT}}). | ||
* Machine learning specific quantities in the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} file: | * Machine learning specific quantities in the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} file: | ||
** Estimation of required memory per core. It is written at the beginning of the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} before allocations are done (see [[ML_LOGFILE#Memory consumption estimation|here]]). It is important that if the required memory exceeds the physically available memory the calculation won't necessarily immediately crash at the allocation of static arrays, since many systems use lazy allocations. The calculation could run for a long time before crashing with insufficient memory. Hence the memory estimation should always be checked after startup. | ** Estimation of required memory per core. It is written at the beginning of the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} before allocations are done (see [[ML_LOGFILE#Memory consumption estimation|here]]). It is important that if the required memory exceeds the physically available memory the calculation won't necessarily immediately crash at the allocation of static arrays, since many systems use lazy allocations. The calculation could run for a long time before crashing with insufficient memory. Hence the memory estimation should always be checked after startup. | ||
** <code>STATUS</code>: Shows what happened at each molecular-dynamics steps. The force field is updated when the status is "learning/critical". Monitor this variable frequently from the beginning on (<code>grep "STATUS" ML_LOGFILE.1|grep -E 'learning|critical'|grep -v "#"</code>). If the calculation still updates the force field at every step after 50 iterations it is a sign that there is something seriously wrong with the calculation. The same is true if the calculation stops learning after a few steps and only force-field steps are carried out from then on. In both cases, no useful force field will come out. In ideal learning, the frequency of the update of the force field is high at the beginning and continuously decreases until the algorithm learns only sporadically. Note that due to the approximate error prediction of the Bayesian error the learning frequency will never drop to zero. If the learning frequency increases suddenly in the late stages of a molecular dynamics run, it is usually a sign that phase | ** <code>STATUS</code>: Shows what happened at each molecular-dynamics steps. The force field is updated when the status is "learning/critical". Monitor this variable frequently from the beginning on (<code>grep "STATUS" ML_LOGFILE.1|grep -E 'learning|critical'|grep -v "#"</code>). If the calculation still updates the force field at every step after 50 iterations it is a sign that there is something seriously wrong with the calculation. The same is true if the calculation stops learning after a few steps and only force-field steps are carried out from then on. In both cases, no useful force field will come out. In ideal learning, the frequency of the update of the force field is high at the beginning and continuously decreases until the algorithm learns only sporadically. Note that due to the approximate error prediction of the Bayesian error, the learning frequency will never drop to zero. If the learning frequency increases suddenly in the late stages of a molecular dynamics run, it is usually a sign that a new region of phase space is explored, which is currently unknown to the force field. But this sudden increase in learning steps towards the end of training could also indicate unwanted deformations of the system that should be looked into carefully. | ||
** <code>LCONF</code>: Number of local configurations at each learning step. | ** <code>LCONF</code>: Number of local configurations at each learning step. | ||
** <code>ERR</code>: Root mean square error of predicted energy, forces, and stress | ** <code>ERR</code>: Root mean square error of predicted energy, forces, and stress (<math>O</math>) concerning ab-initio data for all training structures up to the current molecular-dynamics step <math>\Delta O=\sqrt{\sum\limits_{N}(O_{\mathrm{AI}}-O_{\mathrm{MLFF}})^{2}/N}</math>. Here <math>N</math> goes over all training structures for the energies, element-wise over each training structure, times the number of atoms per structure times three Cartesian directions for the forces, and element-wise for each training structure times nine tensor components for the stress tensor. | ||
** <code>BEEF</code>: Estimated Bayesian error of energy, forces and stress (columns 3-5). The current threshold for the maximum Bayesian error of forces {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} on column 6. | ** <code>BEEF</code>: Estimated Bayesian error of energy, forces, and stress (columns 3-5). The current threshold for the maximum Bayesian error of forces {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} on column 6. | ||
** <code>THRUPD</code>: Update of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. | ** <code>THRUPD</code>: Update of {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. | ||
** <code>THRHIST</code>: History of Bayesian errors used for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. | ** <code>THRHIST</code>: History of Bayesian errors used for {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. | ||
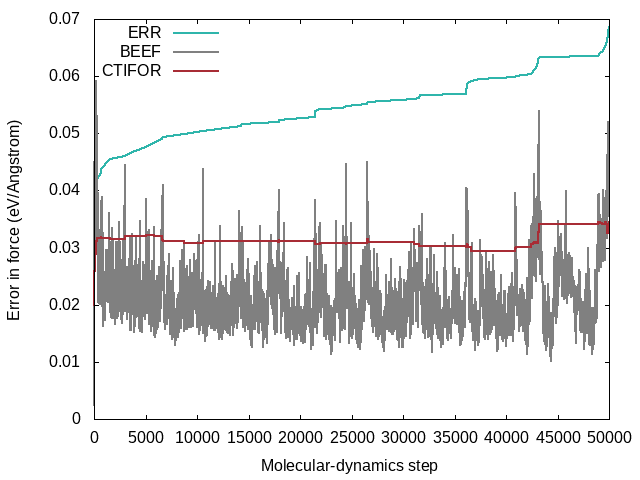
A typical evolution of the real errors (column 4 of <code>ERR</code>), Bayesian errors (column 4 of <code>BEEF</code>) and threshold (column 6 of <code>BEEF</code>) for the forces looks like the following: | A typical evolution of the real errors (column 4 of <code>ERR</code>), Bayesian errors (column 4 of <code>BEEF</code>), and threshold (column 6 of <code>BEEF</code>) for the forces looks like the following: | ||
[[File:ERR BEEF CTIFOR vs MD step.png|500ex]] | [[File:ERR BEEF CTIFOR vs MD step.png|500ex]] | ||
The following commands were used to extract the errors from the {{ | The following commands were used to extract the errors from the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}}: | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-customtoggle-script">'''Click to show commands'''</div> | <div class="toccolours mw-customtoggle-script">'''Click to show commands'''</div> | ||
| Line 122: | Line 143: | ||
* From the plot one can see that the Bayesian errors are always smaller than the real errors. Bayesian inference catches errors in the data well but still retains an error in the probability model. | * From the plot one can see that the Bayesian errors are always smaller than the real errors. Bayesian inference catches errors in the data well but still retains an error in the probability model. | ||
* The plot was extracted from a heating run of liquid water. This can be nicely seen from the steadily increasing real error <code>ERR</code> over the whole calculation. In a constant temperature run the error would usually plateau after some time. | * The plot was extracted from a heating run of liquid water. This can be nicely seen from the steadily increasing real error <code>ERR</code> over the whole calculation. In a constant temperature run the error would usually plateau after some time. | ||
* The steps in the real error correspond to the molecular-dynamics steps where the force | * The steps in the real error correspond to the molecular-dynamics steps where the force field is updated ('learning' or 'critical' for the <code>STATUS</code>). This would be also evident from the change in the number of local reference configurations (<code>grep "LCONF" ML_LOGFILE</code>) at the same molecular-dynamics steps. | ||
* The following things can cause an increase in errors: | |||
** Using a temperature ramp always results in steadily increasing errors. | |||
** A sudden increase in errors (especially after being stable for some time) usually indicates deformations of the cell. Usually one wants to avoid these deformations and only train the "collective vibrations" of a given phase at different temperatures. Common causes of these deformations are too large temperatures leading to phase transitions or neglect of constraints ({{FILE|ICONST}} file) for liquids. | |||
** The evidence approximation is over-fitting and the regularization cannot handle the over-fitting. This is a rare case, but if it happens one should start to reduce the fitting data by increasing {{TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}}. | |||
== Testing and application == | |||
When running force-field-only calculations ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=RUN) set the ab-initio parameters to small values (this is automatically done for some tags, i.e. {{TAG|ENCUT}}). {{VASP}} cannot circumvent the initialization of KS orbitals although they are not used during the molecular dynamics run with machine learning. | |||
=== Spilling factor: error estimates during production runs=== | |||
Using the [[Machine learning force field: Theory#Spilling factor|spilling factor]] one can measure the error during the production runs. To do so one has to set the following in the {{TAG|INCAR}} file (the default value is 0) | |||
{{TAGBL|ML_IERR}}>0 | |||
This tag controls after how many molecular dynamics steps the [[Machine learning force field: Theory#Spilling factor|spilling factor]] is calculated. The calculation of the spilling factor scales quadratically with the number of local reference configurations and linearly with the number of species. So for force fields containing many species and/or local reference configurations, the evaluation time of the spilling factor becomes of the order of magnitude or more as the evaluation of a single force field step. Since it is enough to monitor the error only after the ions moved several MD steps, the total time consumed by evaluating the spilling factor can become insignificantly compared to the total time. So in long molecular dynamics calculations, we recommend using at least {{TAG|ML_IERR}}=20-100. | |||
The [[Machine learning force field: Theory#Spilling factor|spilling factor]] measures the similarity of the local environment of each atom in the current structure to that of the local reference configurations of the force field. The values of the spilling factor are in the range <math>[0,1]</math>. lf the atomic environment is "properly" represented by the local reference configurations the spilling factor approaches 0. Vice versa the spilling factor approaches quickly 1, meaning that the force field is probably extrapolating. Molecular dynamics trajectories where the spilling factor is most of the time 1 can still lead to good results, but the calculations should be cautiously used. | |||
Besides being able to monitor the accuracy during the production runs one can also use the spilling factor to assess the accuracy of the force field for given test sets (i.e. structures chosen from ensembles at different temperatures) like in the traditional way, where test structures are picked out and ab initio calculations have to be carried out for each structure. Using the spilling factor the error is directly assessed without the need for ab initio calculations making the procedure orders of magnitude faster and easier to handle (no evaluation script needed). Nevertheless, if one wants to measure the true error on a test set we have described how to [[Best practices for machine-learned force fields#Test errors|below]]. | |||
=== | === Test errors === | ||
To assess the predictive power of your MLFF, start by generating a test set reflecting the conditions your force field will encounter. A good way to get test structures is to conduct a molecular dynamics (MD) run using the MLFF and then extract a chosen number of structures equidistantly from the {{FILE|XDATCAR}} file. Next, carry out ab-initio calculations for these structures. Be very careful to use exactly the same ab-initio parameters that were used for training. Otherwise in the worst case, one would compare apples with oranges. The longer the trajectory and the higher the number of chosen structures the better the testing, but of course at a higher computational cost due to the increased number of MD steps and ab-initio calculations. | |||
For a comprehensive error analysis, compare ab-initio forces, stress, and energies with MLFF predictions. Below is a code snippet utilizing {{py4vasp}} to guide your analysis: | |||
from py4vasp import MLFFErrorAnalysis | |||
from py4vasp import plot | |||
import numpy as np | |||
# Compute the errors | |||
mlff_error_analysis = MLFFErrorAnalysis.from_files( | |||
dft_data="./test_set/DFTdata/*.h5", | |||
mlff_data="./e01_error_analysis/MLFF_data/*.h5" | |||
) | |||
energy_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_energy_error_per_atom() | |||
# force_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_force_rmse() | |||
# stress_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_stress_rmse() | |||
x = np.arange(len(energy_error)) | |||
plot(x, energy_error, ylabel="Energy error [eV/atom]", xlabel="Configuration Number") | |||
Assess the agreement between ab-initio reference and MLFF by testing specific physical properties. Consider properties like radial distribution functions, relaxed lattice parameters, phonons, elastic constants, relative energies of phases and defect formation energies, to name a few. | |||
=== Monitoring MLFF run with blocked averages === | |||
In each application, it is essential to carefully control the ensemble conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and volume. Achieving a specific condition requires allowing the system sufficient time to relax, typically measured in a minimum number of molecular dynamics steps. Determining the appropriate number of these steps becomes a crucial consideration in the optimization of MD simulations. Ideally, one could look directly at the observable or its mean value and observe that after a given number of steps the observable would not change anymore. Unfortunately, this is not easy in many cases since observables like temperature, pressure, and volume undergo many fluctuations. | |||
An alternative way to monitor the convergence of the observables is via statistical methods. For that block averages are a very good method. Explaining the method here would go beyond the scope of this paragraph, but the theory and the implementation of the method are nicely explained in appendix D3 of Ref. {{cite|frenkel:book:1996}}. At the moment the user has to implement this post-calculation analysis himself, but we strongly advise to do so. The requirement of having properly relaxed structures is further intensified for [[:Category:Advanced molecular-dynamics sampling| advanced molecular-dynamics sampling methods]]. | |||
== Performance == | |||
The machine learning code is parallelized using MPI. | |||
It is most efficient if scaLAPACK is used since storing (and working on) large matrices, in particular the design matrix, will then be distributed over the MPI ranks. However, a LAPACK-only version exists as well. In the latter case, only a few matrices are stored in a distributed fashion, so due to the high memory demand, the LAPACK version is not feasible for "realistic" systems. | |||
=== Computational efficiency in production runs === | |||
This section addresses challenges encountered in production runs utilizing the force field ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''RUN'') with the fast version (requiring prior refitting using {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''refit''). The time required to evaluate a single step of this force field typically matches the duration needed to write results to files. Furthermore, the file-writing process operates solely in a serial manner. As the number of computational cores increases, the overall time for force field evaluation decreases, while the file-writing time remains constant. Therefore, optimizing performance necessitates adjusting the output frequency. The following flags can be used for that: | |||
*{{TAG|ML_OUTBLOCK}}: This tag determines the minimum step interval for the following output file updates ({{FILE|OSZICAR}}, {{TAG|OUTCAR}}, {{TAG|XDATCAR}}, {{TAG|PCDAT}}, HDF5 and stdout). This tag will possibly change the value of {{TAG|NBLOCK}}, since {{TAG|NBLOCK}} is calculated as MAX({{TAG|ML_OUTBLOCK}}, {{TAG|NBLOCK}}). For large trajectories this tag prevents unnecessarily large output files by controlling data output frequency. | |||
*{{TAG|NBLOCK}}: This tag controls the frequency of the output of {{TAG|PCDAT}} and {{TAG|XDATCAR}}. As written above this tag has at least the same value as {{TAG|ML_OUTBLOCK}}. By setting this tag larger than {{TAG|ML_OUTBLOCK}} the writing of the {{TAG|PCDAT}} and {{TAG|XDATCAR}} will be less frequent than the writing of the remaining files. | |||
*{{TAG|ML_OUTPUT_MODE}}: By setting this tag to 0 the calculation and output of the pair correlation function can be completely turned off. | |||
=== Memory consumption === | |||
To achieve optimal performance, the code utilizes varied array distribution and parallelization strategies. Certain sections are optimized for scaLAPACK with a block-cyclic distribution, resulting in linear memory usage reduction with an increasing number of cores. In particular, the design matrix and covariance matrix follow this distributed storage approach. However, in specific code segments, large data arrays are duplicated across MPI ranks for performance gains. Despite the performance benefits, this practice can rapidly increase memory consumption to prohibitive levels (several GB per core), particularly on high-core-count nodes. To tackle this issue, we have introduced the option to store these arrays in [[shared memory]]. With this approach, each node writes these arrays into memory once, enabling all cores on the node to have reading access to them. We strongly recommend activating this feature by adding the following precompiler option to the list of precompiler options: <code>-Duse_shmem</code>. | |||
The estimated memory is found in the first section of the {{TAG|ML_LOGFILE}} and contains an '''estimation''' of memory requirements based on {{VASP}} files read on startup. In the simplest case ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''TRAIN'' with no {{FILE|ML_AB}} file present) it depends on the settings in the {{FILE|INCAR}} and {{FILE|POSCAR}} file. For example, the expected memory consumption may strongly vary with the number of elements present in the {{FILE|POSCAR}} file. Various {{FILE|INCAR}} tags also influence the memory demand. The two most important are {{TAG|ML_MB}} and {{TAG|ML_MCONF}}. Continuation runs ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''TRAIN'' with {{FILE|ML_AB}} file present) and refitting runs ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''REFIT''), additionally need to store the information from the {{FILE|ML_AB}}, which can be substantial. | |||
A sample output for the memory estimation from the {{FILE|ML_LOGFILE}} looks as follows: | |||
* MEMORY INFORMATION *********************************************************************************************************************** | |||
Estimated memory consumption for ML force field generation (MB): | |||
Persistent allocations for force field : 516.9 | |||
| | |||
|-- CMAT for basis : 20.3 | |||
|-- FMAT for basis : 458.5 | |||
|-- DESC for basis : 2.6 | |||
|-- DESC product matrix : 2.3 | |||
Persistent allocations for ab initio data : 8.1 | |||
| | |||
|-- Ab initio data : 7.8 | |||
|-- Ab initio data (new) : 0.3 | |||
Temporary allocations for sparsification : 460.9 | |||
| | |||
|-- SVD matrices : 460.7 | |||
Other temporary allocations : 15.5 | |||
| | |||
|-- Descriptors : 4.7 | |||
|-- Regression : 6.5 | |||
|-- Prediction : 4.2 | |||
Total memory consumption : 1001.4 | |||
******************************************************************************************************************************************** | |||
While the individual items in the above listing are rather technical the most important number is given in the last line: <code>Total memory consumption</code> approximates the peak memory usage during this {{VASP}} run. However, since not all memory is always allocated at the same time the actual consumption may vary over time. | |||
The following part summarizes which kind of parallelization each part employs: | |||
{{Template:MLFF_memorgy_usage_table}} | |||
The components designated with an ''x'' for scaLAPACK feature block-cyclic distributed arrays, demonstrating nearly perfect scalability with the employed processor count. Increasing the number of processors substantially reduces the required memory for this specific component (It's worth noting that also <code>Descriptors</code> and <code>Prediction</code> will drop in memory, but only slightly since only minor parts of these are distributed). The parts marked with an ''x'' for shared memory show a significant decrease in memory usage if the code is compiled for shared memory (precompiler option ''use_shmem''). | |||
{{NB|mind|This is only an estimate, the actual memory requirement may be even higher. Moreover, this is only the usage for the machine learning part of {{VASP}} which in a training run adds up to the memory of the ab-initio part.}} | |||
{{NB|mind|The most memory-consuming parts (design matrix, covariance matrix) are well distributed over multiple nodes. Hence if one runs out of memory one should try increasing the number of used nodes until the job fits into the combined memory of all nodes.}} | |||
=== Reduction of memory consumption in on-the-fly calculations === | |||
On-the-fly learning can be a very memory-intensive task since both the machine learning and the ab-initio calculations have to share the available memory simultaneously. | |||
This is especially true for systems with an increasing number of elements (4 or more) because the number of local reference configurations has to be sampled for each element. | |||
Here's an attempt to minimize the memory footprint during on-the-fly sampling: | |||
*Minimize the ab-initio parameters required for converged results. Many times the parameters are way past the value that is required for convergence and hence setting these parameters to high values can put a substantial computational overhead on the calculation. In our experience, the following parameters are most likely to fall victim to oversetting: {{TAG|ENCUT}}, {{TAG|PREC}}, and number of k-points. | |||
*If possible use more computational nodes to expand the overall available memory. | |||
*Sample ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''train'') with a low number of maximum local reference configurations that are just enough to keep the trajectories intact for sampling: {{TAG|ML_MB}}=500-1000. | |||
*Following the preceding step, it's probable that the force field is characterized by low accuracy. This situation may lead to a high Bayesian error prediction and an excessive sampling of training structures. A remedy for this is to elevate the Bayesian threshold, {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}}. To achieve this, first modify the Bayesian error criterion to remain constant throughout the calculation by setting {{TAG|ML_ICRITERIA}}=0. Subsequently, inspect the values of Bayesian errors in the [[ML_LOGFILE|ML_LOGFILE]] using the command <code>grep BEEF ML_LOGFILE</code>. Adjust {{TAG|ML_CTIFOR}} so that only a specified percentage of Bayesian errors surpass this set value. | |||
*At this point one has a force field with low accuracy. | |||
*To get an accurate force field (re)select the number of local reference configurations. For this set {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''select'' and increase the maximum number of local reference configurations {{TAG|ML_MB}}. This step needs much more memory but the entire memory is available for the machine learning part since no ab-initio calculations are carried out. | |||
*Last as usual do the refit with {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''refit''. | |||
=== Descriptor reduction in production runs=== | |||
Since in production runs the computational efficiency is hugely determined by the calculation of descriptors and their derivatives, a reduction of the number of three-body descriptors is highly desired. | |||
A straightforward reduction of the number of descriptors by reduction of calculational parameters like {{TAG|ML_MRB2}}, {{TAG|ML_RCUT2}}, etc. would lead to a significant loss of accuracy and is hence not a viable option. | |||
Instead, we can employ reduced descriptors, descriptor sparsification, or a combination of the two. | |||
Both methods will lead to a reduction of accuracy, but up to a given point, the loss of accuracy is small compared to the reduction of the number of descriptors, which leads to a significant speed-up of the calculations. | |||
Descriptor reduction is applied in the refitting of the force field using {{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''refit'', after the training data was collected. That means the {{FILE|INCAR}} tags need to be specified in only that step. In the following production run ({{TAG|ML_MODE}}=''run'') the tags do not need to be specified since they are contained in the {{FILE|ML_FF}} file and used from there. | |||
{{NB|mind| We strongly advice to use the reduced descriptor ({{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}{{=}}1) in mult-component systems.}} | |||
==== Reduced descriptors ==== | |||
The reduced descriptor is selected by specifying {{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}=1. The reduction is done over the number of element types. The standard three-body descriptor scales quadratically with the number of elements. The reduced descriptor scales linearly with the number of element types for several parts of the calculations (but not for all). Also this descriptor seems to be more stable than the standard descriptor. By stability it is meant that the structure is less likely to go onto trajectories that would "blow up" the cell in long molecular dynamics runs. On-the downside this descriptor results in a 5-20% reduced accuracy compared to the standard descriptor. | |||
==== Descriptor sparsification ==== | |||
* {{TAG| | Sparsification of the three-body descriptors is controlled mainly by the following tags: | ||
* {{TAG| | *{{TAG|ML_LSPARSDES}}: This is the main tag and it switches the descriptor sparsification on and off. | ||
*{{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}: This tag controls the extent, by specifying the fraction of remaining descriptors after sparsification. | |||
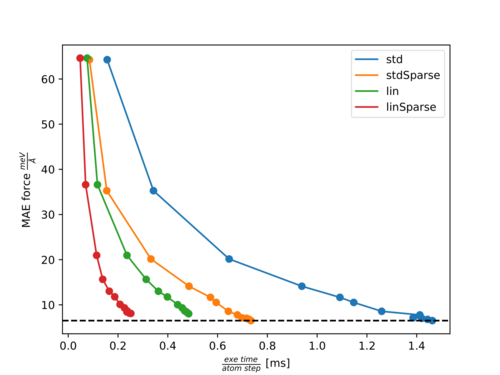
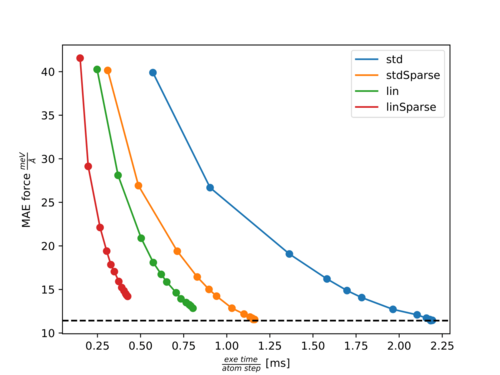
== | In the following two figures, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_front Pareto fronts] (accuracy of forces versus calculation time) for the molecules Ethanol and Azobenzene are shown. | ||
* | The points with increasing accuracy belong to fits with an increasing number of training structures. | ||
The following abbreviations are used: | |||
*''std'': Standard three-body descriptor (default). | |||
*''stdSparse'': Standard three-body descriptor with sparsification of 50% ({{TAG|ML_LSPARSDES}}=''.TRUE.'' and {{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}=0.5). | |||
*''lin'': Element-reduced descriptor involving a linear scaling of several parts with respect to the element types ({{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}=1). | |||
*''linSparse'': Element-reduced descriptor with sparsification of 50% ({{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}=1, {{TAG|ML_LSPARSDES}}=''.TRUE.'' and {{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}=0.5). | |||
Pareto front for Ethanol: | |||
:[[File:Pareto Ethanol.png|500px]] | |||
Pareto front for Azobenzene: | |||
:[[File:Pareto Azobenzene.png|500px]] | |||
For both molecules, there is almost no effect on the accuracy with {{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}=0.5 (50% sparsification) for the standard descriptor while the calculation time per step is almost halved down. This is a good starting point for sparsification of the standard descriptor. However, we recommend the user carefully tests the accuracy loss before using this value blindly. As can be seen from both plots the calculation time is more significantly reduced by {{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}=1 than by {{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}=0.5. This is even more pronounced for denser systems like solids or liquids. This is why we rather advice using the reduced descriptor ({{TAG|ML_DESC_TYPE}}=1) rather than descriptor sparsification ({{TAG|ML_RDES_SPARSDES}}). | |||
The user should be especially cautious when applying sparsification on top of this descriptor because we noticed quite often (as for Azobenzene) that the accuracy decreases faster with an increased amount of sparsification for the reduced descriptor compared to the standard descriptor. This is to some extent also intuitive, since it is harder to throw away ''insignificant'' descriptors from an already reduced or ''sparsified'' pool of descriptors. | |||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
| Line 176: | Line 322: | ||
{{TAGBL|ML_LMLFF}} = .TRUE. | {{TAGBL|ML_LMLFF}} = .TRUE. | ||
{{TAGBL| | {{TAGBL|ML_MODE}} = TRAIN | ||
* {{TAG|ENCUT}}: A larger plane-wave cut-off is used to accommodate possible changes in the lattice parameters | * {{TAG|ENCUT}}: A larger plane-wave cut-off is used to accommodate possible changes in the lattice parameters because an [[NpT ensemble]] is used ({{TAG|ISIF}}=3). | ||
* {{TAG|POMASS}}: Since this structure contains Hydrogen, the mass of Hydrogen is increased by a factor of 8 to be able to use larger integration steps {{TAG|POTIM}}. Without this one possibly needs to use integration steps of {{TAG|POTIM}}<0.5 hugely increasing the computation time. | * {{TAG|POMASS}}: Since this structure contains Hydrogen, the mass of Hydrogen is increased by a factor of 8 to be able to use larger integration steps {{TAG|POTIM}}. Without this one possibly needs to use integration steps of {{TAG|POTIM}}<0.5 hugely increasing the computation time. | ||
* Here {{TAG|GGA}}=RP together with {{ | * Here {{TAG|GGA}}=RP together with {{TAG|IVDW}}=11 is used which gives a good electron exchange and correlation description for liquid water. | ||
{{FILE|ICONST}}: | {{FILE|ICONST}}: | ||
| Line 405: | Line 551: | ||
[[:Category:Machine-learned force fields | Machine-learned force fields]], [[:Category:Ionic minimization| Ionic minimization]], [[:Category:Molecular dynamics|Molecular dynamics]], [[Machine learning force field calculations: Basics]] | [[:Category:Machine-learned force fields | Machine-learned force fields]], [[:Category:Ionic minimization| Ionic minimization]], [[:Category:Molecular dynamics|Molecular dynamics]], [[Machine learning force field calculations: Basics]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
<noinclude> | |||
[[Category:Machine-learned force fields]][[Category:Howto]] | [[Category:Machine-learned force fields]][[Category:Howto]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:59, 18 December 2024
Using the machine-learning-force-fields method, VASP can construct force fields based on ab-initio simulations. When constructing, testing, re-learning, and applying a force field, many aspects must be carefully considered. Some best practices are listed here, but note that the list is not exhaustive and the method has not yet been applied to a large number of systems. We, therefore, recommend the usual rigorous monitoring that is necessary for all research projects. The basic steps required for machine learning force field (MLFF) training can be found on the Basics page on machine learning force field calculations.
Training
Best practice training modes
To start a training run, set ML_MODE = TRAIN. Depending on the existence of a valid ML_AB in the folder where VASP is executed, one of the two modes is automatically selected:
- No ML_AB file: the training algorithm will start from zero.
- ML_AB file is present: Training will continue based on an existing structure database. In this mode of operation, a force field is generated from the existing database (ML_AB file) and then a MD run is continued from the specified POSCAR file. This mode is used to select additional structures from the phase space of the material. But it can also be used to examine surfaces by first training the bulk material, then adding a molecule to the surface in the POSCAR file and continuing the training.
If there are several atoms of the same species which should be treated differently by the machine-learning algorithm it is important to give different names to them in the POSCAR file. For example if there are oxygen atoms in a bulk material and in a molecule at the surface it is advisable to make two groups of oxygen atoms in the POSCAR and call one group O1 and and the second O2.
| Warning: It is not possible to give the same name to different groups of atoms in the POSCAR file and the names are restricted to two characters. |
The training mode requires VASP to perform ab-initio calculations, so the first step is to set up the electronic minimization scheme.
| Warning: It is very important to not change the ab-initio settings in the INCAR file between training from scratch and continuing training. Likewise, the POTCAR file is not allowed to be changed when resuming training. |
Ab-initio calculation setup
In general, everything that applies to VASP DFT calculations also applies here. The guidelines for electronic minimization can be used to set up the ab-initio part for on-the-fly training. Additionally, we strongly advise following these guidelines for ab-initio computation during on-the-fly learning:
- Do not set MAXMIX>0 when using force fields for machine learning. During machine learning, first-principles calculations are often bypassed for hundreds or even thousands of ion steps, and ions can move significantly between first-principles calculations. In these cases, the use of MAXMIX very often results in non-converged electronic structures or errors during the self-consistency cycle.
- It is generally possible to train force fields on a smaller unit cell and then apply them to a larger system. Be sure to choose a large enough structure so that the phonons or collective oscillations "fit" into the supercell.
- It is important to learn the exact forces. To do this, the electronic minimization has to be checked for convergence. These checks may include, for example, the number of k-points in the KPOINTS file, the plane wave limit (ENCUT), the electronic minimization algorithm, etc.
- Turn off symmetry as for standard molecular dynamics runs (ISYM=0).
- For simulations without a fixed grid (NpT), the cutoff for plane waves ENCUT must be set at least 30 percent higher than for fixed volume calculations. Also, it is good to restart frequently (ML_MODE=TRAIN with existing ML_AB file in working directory) to reinitialize the PAW basis of KS orbitals and avoid Pulay stress.
Molecular dynamics setup
After the forces are obtained from electronic minimization by the Hellmann-Feynman Theorem, VASP must propagate the ions to obtain a new configuration in phase space. For the molecular dynamics part, familiarity with setting up molecular dynamics runs is beneficial. In addition, we recommend the following settings in the molecular dynamics part:
- Decrease the integration step (POTIM) if the system contains light elements, or increase the light element mass (POMASS) in the INCAR or the POTCAR file. As a rule of thumb, the time step should not exceed 0.7 fs and 1.5 fs for hydrogen and oxygen-containing compounds, respectively. However, a time step of 3 fs may work well for heavy elements (Si).
- If possible, heat the system gradually using the temperature ramp (set TEEND higher than TEBEG). Start with a low temperature (not zero) and increase it to a temperature about 30% above the desired application temperature. This will help "on-the-fly" training to explore a larger portion of the phase space and will result in more stable force fields.
- If possible, prefer molecular dynamics training runs in the NpT ensemble (ISIF=3). The additional cell fluctuations improve the robustness of the resulting force field. However, for fluids, only volume changes of the supercell are allowed, otherwise, the cell may "collapse", i.e., it tilts extremely so that the system becomes a layer of atoms. This can be achieved with ICONST, here and here. For an example input for constraining the cell shape, see the ICONST page or the end of this page page. The NVT ensemble (ISIF=2) is also acceptable for training, but use the Langevin thermostat as it is very good for phase space sampling (ergodicity) due to its stochastic nature.
- One should always try to explore as much of the phase space of the material as possible. Therefore, one should always avoid training in the NVE ensemble.
General settings for on the fly training
The ML_MODE=TRAIN sets already widely used default values for on-the-fly training in machine learning. Nevertheless, we would like to provide the following guidelines for setting individual machine-learning parameters:
- If the system contains different components, first train them separately. For example, if the system consists of a crystal surface and a molecule that binds to that surface. Train the main crystal first, then the surface, possibly the isolated molecule, and finally the entire system (if you do not need to describe the isolated molecule, you can skip training for the molecule). In this way, a considerable number of ab-initio calculations can be avoided in the most computationally intensive combined system.
- If you train a system containing a surface or isolated molecules do not train the stresses. For that set ML_WTSIF to a very small value in the INCAR file (e.g. ML_WTSIF=1E-10). In surface calculations, the surface is terminated by a vacuum layer which does not exert stress onto the cell. Isolated molecules are similar since they are vacuum terminated in all directions. Hence, these simulations have to be done in the NVT or NVE ensemble.
- If there are not enough reference configurations taken during training (seen in ML_ABN), adjusting the default value of ML_CTIFOR=0.02 to a lower value is advisable. The value of this flag is highly dependent on the system under consideration, so it is encouraged to determine the correct value of this flag by trial and error.
- A force field is only ever applicable to the phases of the material in which it has been trained. Therefore, machine-learned force fields cannot be expected to provide reliable results for conditions for which training data have not been collected.
Retraining with re-selection of local reference configurations
This mode is selected with ML_MODE=SELECT. In this mode, a new machine-learned force field is generated from the ab-initio data provided in the ML_AB file. The structures are read in and processed sequentially as if they had been obtained through an MD simulation. In other words, the same steps are performed as in on-the-fly training, but the data source is not an MD run, but the structures available in the ML_AB file. This mode of operation can be used to generate VASP force fields for machine learning from precomputed or external ab-initio datasets. The main difference with ML_ISTART = REFIT is that the list of local reference configurations in the ML_AB file is ignored and a new set is created. The newly updated set is written to the final file ML_ABN. If the calculations for ML_MODE = SELECT are too time-consuming with the default settings, it is useful to increase ML_MCONF_NEW to values around 10-16 and set ML_CDOUB = 4. This often speeds up calculations by a factor of 2-4. The automatic update of ML_CTIFOR is not very stable at the beginning of the reselection if the force fields are not sampled sufficiently and are therefore inaccurate. Then a too-high value for ML_CTIFOR may be determined and in all later steps the errors of the predicted forces would be below ML_CTIFOR. Therefore, no training would be performed. To address this, ML_MODE=SELECT does not apply any update for ML_CTIFOR by default (ML_ICRITERIA = 0). Also, it can be beneficial to vary ML_CTIFOR until a satisfactory number of local reference configurations is found (i.e. until the matching errors stop decreasing as the number of local reference configurations increases). The number of local reference configurations increases as ML_CTIFOR becomes smaller. It is strongly recommended to perform a more accurate SVD-based refitting afterward.
Retraining with hyper-parameter optimization
After you have collected a sufficient number of local atomic reference configurations, as described in Training from scratch and Continuation training, it is recommended to optimize the parameters for your force field. This will result in lower training and test set errors. The reference configurations selected in the ML_AB will not be updated. To perform a hyperparameter search, ML_MODE=REFIT must be set in the INCAR file and a ML_AB must exist in the working directory. By setting ML_MODE=REFIT, VASP automatically selects ML_IALGO_LINREG=4, which performs a regularized SVD to find the appropriate weights (see here for the definition). It is favorable to enter refit mode and tune the hyperparameters to improve the fitting error, which can be found in the ML_LOGFILE under the description ERR. To tune the hyperparameters, set the desired parameter in the INCAR file, then run VASP and check the error in the ML_LOGFILE. For more information on extracting errors from the ML_LOGFILE, see here. Adjusting the following parameters may improve the quality of the force-fields:
- Adjusting the cutoff radius for the angular and radial descriptor by adjusting ML_RCUT2 and ML_RCUT1.
- Matching the number of radial and angular basis functions with ML_MRB1 and ML_MRB2.
- The parameter ML_LMAX2 should be optimized to obtain the maximum angular quantum number for spherical harmonics.
- The regularization parameter for the SVD can be adjusted by setting ML_SIGW0 in the INCAR. The regularization should always be set as large as possible so that the force field can be applied to structures outside of the training set.
- {TAG|ML_EPS_LOW}} should be used to sparsify the local reference configurations used from the ML_AB. This can improve the performance of the trained force field. However, it may also reduce the accuracy.
| Mind: Hyperparameter optimization should always be started from default values |
| Mind: For fluids, reducing to ML_LMAX2=2 and ML_RCUT2=4 can lead to better fitting results. |
Accuracy
The achievable accuracy of the force fields depends on many factors, e.g. species, temperature, pressure, electronic convergence, machine learning method, etc. In our implementation of kernel ridge regression, the accuracy of the force fields increases as the number of local reference configurations increases. This increase is not linear and at the same time, the computational cost increases linearly. When generating machine-learning force fields there is always a tradeoff between accuracy and efficiency.
Here are some empirical guidelines:
- For a given structure, the error increases with increasing temperature and pressure. Therefore, the force field should not be trained under conditions too far from the target condition. For example, for a production run at 300 K, it is good to learn above this temperature (450-500 K) to capture more structures that might occur in the production run, but it is not beneficial to learn the same phase at, say, 1000 K, as this is likely to reduce the accuracy of the force field.
- Liquids typically require many more training structures and local reference configurations to achieve similar accuracy to solids. To achieve errors of about 30 meV/angstrom, liquids often require 2000-4000 local reference configurations, while 500-1000 reference configurations might be sufficient for simple periodic volume systems.
- Typically, the fitting errors should be less than 1 meV/atom for the energies and 30-100 meV/angstrom for the forces at temperatures between 300-1000 K. Errors slightly above these values may be acceptable, but these calculations should be thoroughly checked for accuracy.
Accurate force fields
The default parameters that control learning and sampling are chosen to provide a good tradeoff between accuracy and efficiency. In particular, the default setting for ML_EPS_LOW tends to remove local reference configurations during the sparsification step, limiting accuracy. However, further decreasing ML_EPS_LOW to values below 1.0E-11 does not improve accuracy, since the condition number of the regularized normal equation solved in Bayesian regression is approximately proportional to the square of the condition number of the Gram matrix considered during sparsification (see here). Thus, if the Gram matrix has a condition number of 1E9, then the normal equation has a condition number of 1E18, which means that a loss of significance occurs when the normal equation is solved.
To obtain highly accurate force fields that retain more local reference configurations, one must use the following two-step procedure:
First, one performs a full on-the-fly learning:
ML_IALGO_LINREG=1; ML_SION1=0.3; ML_MRB2=12
This can consist of many different training steps that include all the desired structures. Increasing ML_MRB1 from 8 to 12 and decreasing ML_SION1 from 0.5 to 0.3 improves the condition number of the Gram matrix by about a factor of 10 and allows the sparsification step to retain more local reference configurations (typically by about a factor of 2). Of course, this slows down the force field calculations somewhat.
If full retraining is not possible, you can also try to increase only the number of local reference calculations, as described above, by using ML_MODE=SELECT and choosing a value for ML_CTIFOR that gives a satisfactory number of local reference configurations.
Second, readjust the force field using ML_MODE=REFIT.
Using SVD instead of solving the regularized normal equation avoids squaring the problem, and therefore the condition number of the design matrix rather than its square is important. In our experience, SVD refinement with the default value ML_SION1=0.5 always improves the accuracy of the force field.
Tuning on-the-fly parameters
In case too many or too few training structures and local reference configurations are selected some on-the-fly parameters can be tuned (for an overview of the learning and threshold algorithms we may refer here):
- ML_CTIFOR: Defines the learning threshold for the Bayesian error of the forces for each atom. In a continuation run, it can be set to the last value of ML_CTIFOR of the previous run. This way unnecessary sampling at the beginning of the calculation can be skipped. However, when going from one structure to the other, this tag should be very carefully set. ML_CTIFOR is species and system dependent. Low symmetry structures, for example, liquids, have usually a much higher error than high symmetry solids for the same compound. If a liquid is learned first and the last ML_CTIFOR from the liquid is used for the corresponding solid, this ML_CTIFOR is way too large for the solid and all predicted errors will be below the threshold. Hence no learning will be done on the solid. In this case, it is better to start with the default value for ML_CTIFOR. Typical attainable values for ML_CTIFOR are 0.02 around 300-500 K, and 0.06 around 1000-2000 K, so temperature but also system dependent.
- ML_CX: It is involved in the calculation of the threshold, ML_CTIFOR = (average of the stored Bayesian errors in the history) *(1.0 + ML_CX). This tag affects the frequency of selection of training structures and local reference configurations. Positive values of ML_CX result in a less frequent sampling (and hence less ab-initio calculations) and negative values result in the opposite. Typical values of ML_CX are between -0.3 and 0. For training runs using heating, the default usually results in very well-balanced machine-learned force fields. When the training is performed at a fixed temperature, it is often desirable to decrease to ML_CX=-0.1, to increase the number of first principle calculations, and thus the size of the training set (the default can result in too few training data).
- ML_MHIS: Sets the number of previous Bayesian errors (from learning steps for the default of ML_ICRITERIA) that are used for the update of ML_CTIFOR. If, after the initial phase, strong variations of the Bayesian errors between updates of the threshold appear and the threshold also changes strongly after each update, the default of 10 for this tag can be lowered.
- ML_SCLC_CTIFOR: Scales ML_CTIFOR only in the selection of local reference configurations. In contrast, to ML_CX this tag does not affect the frequency of sampling (ab-initio calculations). Smaller values mean more local reference configurations are selected; large values mean fewer local reference configurations are selected.
- ML_EPS_LOW: Controls the sparsification of the number of local reference configurations after they were selected by the Bayesian error estimation. Increasing ML_EPS_LOW increases the number of local reference configurations that are removed and by decreasing the opposite happens. This tag will also not affect the learning frequency since the sparsification is only done after the local reference configurations were selected for a new structure. We do not recommend increasing the threshold to values larger than 1E-7. Below that value this tag works well to control the number of local reference configurations, however, for multi-component systems, the sparsification algorithm tends to lead to strong imbalances in the number of local reference configurations for different species.
- ML_LBASIS_DISCARD: Controls, whether the calculation continues or stops after the maximum number of local reference configurations ML_MB for any species is reached. Previously the default behavior was ML_LBASIS_DISCARD=.FALSE.: the calculation stops and requests an increase of ML_MB if the number of local reference configurations for any species reaches ML_MB. In multi-component systems, the sparse representation for one species exceeds ML_MB very quickly, while the other species are not sufficiently well described by the yet determined local reference configurations and are still far below the limit ML_MB. The present default is hence ML_LBASIS_DISCARD=.TRUE.: In this case, the code disposes of local reference configurations whenever the threshold is reached. It does this species dependent.
Monitoring on-the-fly learning
The monitoring of your learning can be divided into two parts:
- Molecular dynamics/ensemble-related quantities:
- Monitor your structure visually. This means looking at the CONTCAR or XDATCAR files with structure/trajectory viewers. Many times when something goes wrong it can be immediately traced back to unwanted or unphysical deformations.
- Volume and lattice parameters in the OUTCAR, XDATCAR and CONTCAR files. It is important to confirm that the average volume stays in the desired region. A strong change of the average volume over time in constant temperature and pressure runs indicates phase transitions or non-properly equilibrated systems. Particularly troublesome is a strong shearing during a single VASP run: since VASP keeps the plane wave basis set fixed and originally uses a spherical cutoff sphere, the cutoff sphere effectively becomes an ellipsoid. That is, the effective cutoff becomes small in some reciprocal lattice directions. Lattice vector changes of more than 10 % during a single run must be avoided. The corresponding data files ( ML_AB) are not suitable to continue the training (perform your calculations in small "junks").
- Temperature and pressure in the OUTCAR and OSZICAR files. Strong deviations of temperature and pressure to the desired ones at the beginning of the calculation indicate non-properly equilibrated starting positions. If the desired charasteristics undergo strong oscillations optionally block averages can be used to monitor them (for more on block averages please see below under "Application").
- Pair-correlation functions (PCDAT).
- Machine learning specific quantities in the ML_LOGFILE file:
- Estimation of required memory per core. It is written at the beginning of the ML_LOGFILE before allocations are done (see here). It is important that if the required memory exceeds the physically available memory the calculation won't necessarily immediately crash at the allocation of static arrays, since many systems use lazy allocations. The calculation could run for a long time before crashing with insufficient memory. Hence the memory estimation should always be checked after startup.
STATUS: Shows what happened at each molecular-dynamics steps. The force field is updated when the status is "learning/critical". Monitor this variable frequently from the beginning on (grep "STATUS" ML_LOGFILE.1|grep -E 'learning|critical'|grep -v "#"). If the calculation still updates the force field at every step after 50 iterations it is a sign that there is something seriously wrong with the calculation. The same is true if the calculation stops learning after a few steps and only force-field steps are carried out from then on. In both cases, no useful force field will come out. In ideal learning, the frequency of the update of the force field is high at the beginning and continuously decreases until the algorithm learns only sporadically. Note that due to the approximate error prediction of the Bayesian error, the learning frequency will never drop to zero. If the learning frequency increases suddenly in the late stages of a molecular dynamics run, it is usually a sign that a new region of phase space is explored, which is currently unknown to the force field. But this sudden increase in learning steps towards the end of training could also indicate unwanted deformations of the system that should be looked into carefully.LCONF: Number of local configurations at each learning step.ERR: Root mean square error of predicted energy, forces, and stress () concerning ab-initio data for all training structures up to the current molecular-dynamics step . Here goes over all training structures for the energies, element-wise over each training structure, times the number of atoms per structure times three Cartesian directions for the forces, and element-wise for each training structure times nine tensor components for the stress tensor.BEEF: Estimated Bayesian error of energy, forces, and stress (columns 3-5). The current threshold for the maximum Bayesian error of forces ML_CTIFOR on column 6.THRUPD: Update of ML_CTIFOR.THRHIST: History of Bayesian errors used for ML_CTIFOR.
A typical evolution of the real errors (column 4 of ERR), Bayesian errors (column 4 of BEEF), and threshold (column 6 of BEEF) for the forces looks like the following:
The following commands were used to extract the errors from the ML_LOGFILE:
grep ERR ML_LOGFILE|grep -v "#"|awk '{print $2, $4}' > ERR.dat
grep BEEF ML_LOGFILE|grep -v "#"|awk '{print $2, $4}' > BEEF.dat
grep BEEF ML_LOGFILE|grep -v "#"|awk '{print $2, $6}' > CTIFOR.dat
The following gnuplot script was used to plot the errors:
set key left top
set xlabel "Molecular-dynamics step"
set ylabel "Error in force (eV/Angstrom)"
set terminal png
set output 'ERR_BEEF_CTIFOR_vs_MD_step.png'
plot "ERR.dat" using 1:2 with lines lw 2 lt rgb "#2fb5ab" title "ERR", \
"BEEF.dat" using 1:2 with lines lw 2 lt rgb "#808080" title "BEEF", \
"CTIFOR.dat" using 1:2 with lines lw 2 lt rgb "#a82c35" title "CTIFOR"
- From the plot one can see that the Bayesian errors are always smaller than the real errors. Bayesian inference catches errors in the data well but still retains an error in the probability model.
- The plot was extracted from a heating run of liquid water. This can be nicely seen from the steadily increasing real error
ERRover the whole calculation. In a constant temperature run the error would usually plateau after some time. - The steps in the real error correspond to the molecular-dynamics steps where the force field is updated ('learning' or 'critical' for the
STATUS). This would be also evident from the change in the number of local reference configurations (grep "LCONF" ML_LOGFILE) at the same molecular-dynamics steps. - The following things can cause an increase in errors:
- Using a temperature ramp always results in steadily increasing errors.
- A sudden increase in errors (especially after being stable for some time) usually indicates deformations of the cell. Usually one wants to avoid these deformations and only train the "collective vibrations" of a given phase at different temperatures. Common causes of these deformations are too large temperatures leading to phase transitions or neglect of constraints (ICONST file) for liquids.
- The evidence approximation is over-fitting and the regularization cannot handle the over-fitting. This is a rare case, but if it happens one should start to reduce the fitting data by increasing ML_EPS_LOW.
Testing and application
When running force-field-only calculations (ML_MODE=RUN) set the ab-initio parameters to small values (this is automatically done for some tags, i.e. ENCUT). VASP cannot circumvent the initialization of KS orbitals although they are not used during the molecular dynamics run with machine learning.
Spilling factor: error estimates during production runs
Using the spilling factor one can measure the error during the production runs. To do so one has to set the following in the INCAR file (the default value is 0)
ML_IERR>0
This tag controls after how many molecular dynamics steps the spilling factor is calculated. The calculation of the spilling factor scales quadratically with the number of local reference configurations and linearly with the number of species. So for force fields containing many species and/or local reference configurations, the evaluation time of the spilling factor becomes of the order of magnitude or more as the evaluation of a single force field step. Since it is enough to monitor the error only after the ions moved several MD steps, the total time consumed by evaluating the spilling factor can become insignificantly compared to the total time. So in long molecular dynamics calculations, we recommend using at least ML_IERR=20-100.
The spilling factor measures the similarity of the local environment of each atom in the current structure to that of the local reference configurations of the force field. The values of the spilling factor are in the range . lf the atomic environment is "properly" represented by the local reference configurations the spilling factor approaches 0. Vice versa the spilling factor approaches quickly 1, meaning that the force field is probably extrapolating. Molecular dynamics trajectories where the spilling factor is most of the time 1 can still lead to good results, but the calculations should be cautiously used.
Besides being able to monitor the accuracy during the production runs one can also use the spilling factor to assess the accuracy of the force field for given test sets (i.e. structures chosen from ensembles at different temperatures) like in the traditional way, where test structures are picked out and ab initio calculations have to be carried out for each structure. Using the spilling factor the error is directly assessed without the need for ab initio calculations making the procedure orders of magnitude faster and easier to handle (no evaluation script needed). Nevertheless, if one wants to measure the true error on a test set we have described how to below.
Test errors
To assess the predictive power of your MLFF, start by generating a test set reflecting the conditions your force field will encounter. A good way to get test structures is to conduct a molecular dynamics (MD) run using the MLFF and then extract a chosen number of structures equidistantly from the XDATCAR file. Next, carry out ab-initio calculations for these structures. Be very careful to use exactly the same ab-initio parameters that were used for training. Otherwise in the worst case, one would compare apples with oranges. The longer the trajectory and the higher the number of chosen structures the better the testing, but of course at a higher computational cost due to the increased number of MD steps and ab-initio calculations.
For a comprehensive error analysis, compare ab-initio forces, stress, and energies with MLFF predictions. Below is a code snippet utilizing py4vasp to guide your analysis:
from py4vasp import MLFFErrorAnalysis from py4vasp import plot import numpy as np # Compute the errors mlff_error_analysis = MLFFErrorAnalysis.from_files( dft_data="./test_set/DFTdata/*.h5", mlff_data="./e01_error_analysis/MLFF_data/*.h5" ) energy_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_energy_error_per_atom() # force_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_force_rmse() # stress_error = mlff_error_analysis.get_stress_rmse() x = np.arange(len(energy_error)) plot(x, energy_error, ylabel="Energy error [eV/atom]", xlabel="Configuration Number")
Assess the agreement between ab-initio reference and MLFF by testing specific physical properties. Consider properties like radial distribution functions, relaxed lattice parameters, phonons, elastic constants, relative energies of phases and defect formation energies, to name a few.
Monitoring MLFF run with blocked averages
In each application, it is essential to carefully control the ensemble conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and volume. Achieving a specific condition requires allowing the system sufficient time to relax, typically measured in a minimum number of molecular dynamics steps. Determining the appropriate number of these steps becomes a crucial consideration in the optimization of MD simulations. Ideally, one could look directly at the observable or its mean value and observe that after a given number of steps the observable would not change anymore. Unfortunately, this is not easy in many cases since observables like temperature, pressure, and volume undergo many fluctuations. An alternative way to monitor the convergence of the observables is via statistical methods. For that block averages are a very good method. Explaining the method here would go beyond the scope of this paragraph, but the theory and the implementation of the method are nicely explained in appendix D3 of Ref. [1]. At the moment the user has to implement this post-calculation analysis himself, but we strongly advise to do so. The requirement of having properly relaxed structures is further intensified for advanced molecular-dynamics sampling methods.
Performance
The machine learning code is parallelized using MPI. It is most efficient if scaLAPACK is used since storing (and working on) large matrices, in particular the design matrix, will then be distributed over the MPI ranks. However, a LAPACK-only version exists as well. In the latter case, only a few matrices are stored in a distributed fashion, so due to the high memory demand, the LAPACK version is not feasible for "realistic" systems.
Computational efficiency in production runs
This section addresses challenges encountered in production runs utilizing the force field (ML_MODE=RUN) with the fast version (requiring prior refitting using ML_MODE=refit). The time required to evaluate a single step of this force field typically matches the duration needed to write results to files. Furthermore, the file-writing process operates solely in a serial manner. As the number of computational cores increases, the overall time for force field evaluation decreases, while the file-writing time remains constant. Therefore, optimizing performance necessitates adjusting the output frequency. The following flags can be used for that:
- ML_OUTBLOCK: This tag determines the minimum step interval for the following output file updates (OSZICAR, OUTCAR, XDATCAR, PCDAT, HDF5 and stdout). This tag will possibly change the value of NBLOCK, since NBLOCK is calculated as MAX(ML_OUTBLOCK, NBLOCK). For large trajectories this tag prevents unnecessarily large output files by controlling data output frequency.
- NBLOCK: This tag controls the frequency of the output of PCDAT and XDATCAR. As written above this tag has at least the same value as ML_OUTBLOCK. By setting this tag larger than ML_OUTBLOCK the writing of the PCDAT and XDATCAR will be less frequent than the writing of the remaining files.
- ML_OUTPUT_MODE: By setting this tag to 0 the calculation and output of the pair correlation function can be completely turned off.
Memory consumption
To achieve optimal performance, the code utilizes varied array distribution and parallelization strategies. Certain sections are optimized for scaLAPACK with a block-cyclic distribution, resulting in linear memory usage reduction with an increasing number of cores. In particular, the design matrix and covariance matrix follow this distributed storage approach. However, in specific code segments, large data arrays are duplicated across MPI ranks for performance gains. Despite the performance benefits, this practice can rapidly increase memory consumption to prohibitive levels (several GB per core), particularly on high-core-count nodes. To tackle this issue, we have introduced the option to store these arrays in shared memory. With this approach, each node writes these arrays into memory once, enabling all cores on the node to have reading access to them. We strongly recommend activating this feature by adding the following precompiler option to the list of precompiler options: -Duse_shmem.
The estimated memory is found in the first section of the ML_LOGFILE and contains an estimation of memory requirements based on VASP files read on startup. In the simplest case (ML_MODE=TRAIN with no ML_AB file present) it depends on the settings in the INCAR and POSCAR file. For example, the expected memory consumption may strongly vary with the number of elements present in the POSCAR file. Various INCAR tags also influence the memory demand. The two most important are ML_MB and ML_MCONF. Continuation runs (ML_MODE=TRAIN with ML_AB file present) and refitting runs (ML_MODE=REFIT), additionally need to store the information from the ML_AB, which can be substantial.
A sample output for the memory estimation from the ML_LOGFILE looks as follows:
* MEMORY INFORMATION *********************************************************************************************************************** Estimated memory consumption for ML force field generation (MB): Persistent allocations for force field : 516.9 | |-- CMAT for basis : 20.3 |-- FMAT for basis : 458.5 |-- DESC for basis : 2.6 |-- DESC product matrix : 2.3 Persistent allocations for ab initio data : 8.1 | |-- Ab initio data : 7.8 |-- Ab initio data (new) : 0.3 Temporary allocations for sparsification : 460.9 | |-- SVD matrices : 460.7 Other temporary allocations : 15.5 | |-- Descriptors : 4.7 |-- Regression : 6.5 |-- Prediction : 4.2 Total memory consumption : 1001.4 ********************************************************************************************************************************************
While the individual items in the above listing are rather technical the most important number is given in the last line: Total memory consumption approximates the peak memory usage during this VASP run. However, since not all memory is always allocated at the same time the actual consumption may vary over time.
The following part summarizes which kind of parallelization each part employs:
scaLAPACK shared memory CMAT for basis x x FMAT for basis x DESC for basis x x DESC product matrix x Ab initio data Ab initio data (new) SVD matrices x Descriptors Regression x Prediction
The components designated with an x for scaLAPACK feature block-cyclic distributed arrays, demonstrating nearly perfect scalability with the employed processor count. Increasing the number of processors substantially reduces the required memory for this specific component (It's worth noting that also Descriptors and Prediction will drop in memory, but only slightly since only minor parts of these are distributed). The parts marked with an x for shared memory show a significant decrease in memory usage if the code is compiled for shared memory (precompiler option use_shmem).
| Mind: This is only an estimate, the actual memory requirement may be even higher. Moreover, this is only the usage for the machine learning part of VASP which in a training run adds up to the memory of the ab-initio part. |
| Mind: The most memory-consuming parts (design matrix, covariance matrix) are well distributed over multiple nodes. Hence if one runs out of memory one should try increasing the number of used nodes until the job fits into the combined memory of all nodes. |
Reduction of memory consumption in on-the-fly calculations
On-the-fly learning can be a very memory-intensive task since both the machine learning and the ab-initio calculations have to share the available memory simultaneously. This is especially true for systems with an increasing number of elements (4 or more) because the number of local reference configurations has to be sampled for each element.
Here's an attempt to minimize the memory footprint during on-the-fly sampling:
- Minimize the ab-initio parameters required for converged results. Many times the parameters are way past the value that is required for convergence and hence setting these parameters to high values can put a substantial computational overhead on the calculation. In our experience, the following parameters are most likely to fall victim to oversetting: ENCUT, PREC, and number of k-points.
- If possible use more computational nodes to expand the overall available memory.
- Sample (ML_MODE=train) with a low number of maximum local reference configurations that are just enough to keep the trajectories intact for sampling: ML_MB=500-1000.
- Following the preceding step, it's probable that the force field is characterized by low accuracy. This situation may lead to a high Bayesian error prediction and an excessive sampling of training structures. A remedy for this is to elevate the Bayesian threshold, ML_CTIFOR. To achieve this, first modify the Bayesian error criterion to remain constant throughout the calculation by setting ML_ICRITERIA=0. Subsequently, inspect the values of Bayesian errors in the ML_LOGFILE using the command
grep BEEF ML_LOGFILE. Adjust ML_CTIFOR so that only a specified percentage of Bayesian errors surpass this set value. - At this point one has a force field with low accuracy.
- To get an accurate force field (re)select the number of local reference configurations. For this set ML_MODE=select and increase the maximum number of local reference configurations ML_MB. This step needs much more memory but the entire memory is available for the machine learning part since no ab-initio calculations are carried out.
- Last as usual do the refit with ML_MODE=refit.
Descriptor reduction in production runs
Since in production runs the computational efficiency is hugely determined by the calculation of descriptors and their derivatives, a reduction of the number of three-body descriptors is highly desired. A straightforward reduction of the number of descriptors by reduction of calculational parameters like ML_MRB2, ML_RCUT2, etc. would lead to a significant loss of accuracy and is hence not a viable option. Instead, we can employ reduced descriptors, descriptor sparsification, or a combination of the two. Both methods will lead to a reduction of accuracy, but up to a given point, the loss of accuracy is small compared to the reduction of the number of descriptors, which leads to a significant speed-up of the calculations.
Descriptor reduction is applied in the refitting of the force field using ML_MODE=refit, after the training data was collected. That means the INCAR tags need to be specified in only that step. In the following production run (ML_MODE=run) the tags do not need to be specified since they are contained in the ML_FF file and used from there.
| Mind: We strongly advice to use the reduced descriptor (ML_DESC_TYPE=1) in mult-component systems. |
Reduced descriptors
The reduced descriptor is selected by specifying ML_DESC_TYPE=1. The reduction is done over the number of element types. The standard three-body descriptor scales quadratically with the number of elements. The reduced descriptor scales linearly with the number of element types for several parts of the calculations (but not for all). Also this descriptor seems to be more stable than the standard descriptor. By stability it is meant that the structure is less likely to go onto trajectories that would "blow up" the cell in long molecular dynamics runs. On-the downside this descriptor results in a 5-20% reduced accuracy compared to the standard descriptor.
Descriptor sparsification
Sparsification of the three-body descriptors is controlled mainly by the following tags:
- ML_LSPARSDES: This is the main tag and it switches the descriptor sparsification on and off.
- ML_RDES_SPARSDES: This tag controls the extent, by specifying the fraction of remaining descriptors after sparsification.
In the following two figures, Pareto fronts (accuracy of forces versus calculation time) for the molecules Ethanol and Azobenzene are shown. The points with increasing accuracy belong to fits with an increasing number of training structures. The following abbreviations are used:
- std: Standard three-body descriptor (default).
- stdSparse: Standard three-body descriptor with sparsification of 50% (ML_LSPARSDES=.TRUE. and ML_RDES_SPARSDES=0.5).
- lin: Element-reduced descriptor involving a linear scaling of several parts with respect to the element types (ML_DESC_TYPE=1).
- linSparse: Element-reduced descriptor with sparsification of 50% (ML_DESC_TYPE=1, ML_LSPARSDES=.TRUE. and ML_RDES_SPARSDES=0.5).
Pareto front for Ethanol:
Pareto front for Azobenzene:
For both molecules, there is almost no effect on the accuracy with ML_RDES_SPARSDES=0.5 (50% sparsification) for the standard descriptor while the calculation time per step is almost halved down. This is a good starting point for sparsification of the standard descriptor. However, we recommend the user carefully tests the accuracy loss before using this value blindly. As can be seen from both plots the calculation time is more significantly reduced by ML_DESC_TYPE=1 than by ML_RDES_SPARSDES=0.5. This is even more pronounced for denser systems like solids or liquids. This is why we rather advice using the reduced descriptor (ML_DESC_TYPE=1) rather than descriptor sparsification (ML_RDES_SPARSDES). The user should be especially cautious when applying sparsification on top of this descriptor because we noticed quite often (as for Azobenzene) that the accuracy decreases faster with an increased amount of sparsification for the reduced descriptor compared to the standard descriptor. This is to some extent also intuitive, since it is harder to throw away insignificant descriptors from an already reduced or sparsified pool of descriptors.
Example
Sample input for learning of liquid water in the NpT ensemble at 0.001 kB using a temperature ramp.
ENCUT = 700 #larger cutoff LASPH = .True. GGA = RP IVDW = 11 ALGO = Normal LREAL = Auto ISYM = 0 IBRION = 0 MDALGO = 3 ISIF = 3 POTIM = 1.5 TEBEG = 200 TEEND = 500 LANGEVIN_GAMMA = 10.0 10.0 LANGEVIN_GAMMA_L = 3.0 PMASS = 100 PSTRESS = 0.001 NSW = 20000 POMASS = 8.0 16.0 ML_LMLFF = .TRUE. ML_MODE = TRAIN
- ENCUT: A larger plane-wave cut-off is used to accommodate possible changes in the lattice parameters because an NpT ensemble is used (ISIF=3).
- POMASS: Since this structure contains Hydrogen, the mass of Hydrogen is increased by a factor of 8 to be able to use larger integration steps POTIM. Without this one possibly needs to use integration steps of POTIM<0.5 hugely increasing the computation time.
- Here GGA=RP together with IVDW=11 is used which gives a good electron exchange and correlation description for liquid water.
LA 1 2 0 LA 1 3 0 LA 2 3 0 LR 1 0 LR 2 0 LR 3 0 S 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 S 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 S 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 S 0 0 0 1 -1 0 0 S 0 0 0 1 0 -1 0 S 0 0 0 0 1 -1 0
- Since a liquid in the NpT ensemble is simulated here, the ICONST file ensures that the lattice parameters are allowed to change to accommodate the pressure, but the length ratio and angles between the lattice parameters remain constant. This prevents unwanted deformations of the cell.
H2O_liquid
1.00000000000000
12.5163422232076691 0.0000233914035418 0.0000148478021513
0.0000000000114008 12.5162286489880472 0.0000199363611203
0.0000000000209813 0.0000000000005105 12.5176610723470780
H O
126 63
Direct
0.2282617284551465 0.0100328590137529 -0.1126387890656106
0.9746403004006459 -0.2476460083611154 -0.2607428157584675
0.5495157277709571 0.8457364197593650 -0.2477873147502692
0.8285605776747957 1.3957130438711647 0.3236429564827718
0.7772914822330327 0.4827858883979471 0.6904243173615018
0.0577768259920047 0.2223168123471880 -0.7608749959673696
0.9446580715027482 1.1212973211581765 0.3550426042339572
0.8506873790066947 0.1718425528358722 0.6288341575238712
0.6762596340888892 0.6505044169314104 0.2894195166948972
0.5611370443226182 -0.0333524123727857 0.5214208317960167
0.6816550720303126 -0.1211211829857703 0.4073898872723471
0.9980109015831524 0.4469736864199069 0.7701748771760492
0.6678832112330954 0.5234479361650100 0.1656392748166443
0.5040346446185426 0.5390736385800624 0.3470193329922442
0.6410360744431883 1.2034330133853826 -0.5204809500538871
0.5009140032853824 1.0194465602602765 0.0680968735186743
1.1286687923693957 0.4815796673077014 0.1056405447614227
1.3281242572016398 -0.0586744504576348 1.2791126768723411
1.2745979045721432 0.6605001257033906 0.1708686731589134
0.4889175843208496 0.3992133071729653 0.6662361557283188
1.1680688935402925 0.7448174915883062 0.4840737703429457
0.5441535549963540 1.2562238170486451 -0.1933215921435651
0.7539782822013665 0.4393165162255908 -0.1111210880770900
0.7158370742172643 0.2516648581738293 0.0129481804279206
0.2713582658190841 0.2279864583332417 -0.2165119651431964
0.9024539921023629 -0.1184662408708287 0.6213800486657953
0.4615161508482398 0.2475213172787736 0.4504737358928211
1.0118559400607643 0.7424282505541469 0.0746984790656740
0.2903967612053814 0.3755361842352651 0.5760967580335238
0.3231287130417146 0.7657698148287657 -0.4355073700974863
1.0376988097955901 0.0758439375796752 -0.0755636247212518
0.3490021766854268 -0.0144512406004137 -0.1286563387493205
0.9105647459905236 0.7180137269788829 -0.1630338422998813
0.6217984736501840 0.7636375746785418 -0.2985814512057716
0.7745581203120666 1.3708044347688073 0.2161898767275624
0.6604329281507487 0.4588369178206191 0.6638505715678867
0.9367092142161492 0.2566478031322914 -0.7657152701827817
0.9210696992439242 1.0100086011945200 0.3831186344742445
0.7198461947247682 0.1832700676815498 0.6289634217232680
0.5794490968641994 0.6650526418110994 0.2084878611072036
0.4451295011889302 0.0227193097626150 0.5285299460037345
0.6493078638087474 -0.2119508709082261 0.4952750816523580
0.9786031188935814 0.5691499073939285 0.7498421879775161
0.7284271721290199 0.4873101999963645 0.0606006569966631
0.4910977185777734 0.5607404559463554 0.4688446654579101
0.5685724756690831 1.1303057766954432 -0.4520626434287254
0.5834889098964630 0.9606882347596553 0.0036536368035990
1.0401204359334022 0.5623696717124362 0.0540990885930118
1.2824173065014235 0.0145062237175715 1.3666813391539134
0.3486617682267537 -0.2934149709168444 0.0822130144717180
0.5730104678470570 0.3084776512554136 0.6220956625895938
0.0696111366994306 0.7429990748207962 0.4037397615014190
0.5502677722150517 1.2295680823859727 -0.0773553830031266
0.6629391487219132 0.5328361705119534 -0.1150519950062741
0.6250848388543612 0.3083123187101773 0.0765665590910336
0.3662802395551557 0.2702906914452067 -0.1383165019423200
0.9736705556543800 -0.1799052283389148 0.5343666577034214
0.4295248327300012 0.3704736742659817 0.4332641348308674
0.8980973959825628 0.6990554008415506 0.0343927673672955
0.2875819013957733 0.4057639685103899 -0.3043930746820226
0.2339822436285078 0.7745846329456394 0.6458551118383669
1.0595055035190402 -0.0564894402119362 -0.0902725095487327
0.8934974071042586 0.3290512561302191 0.8603972804418396
0.5553026810346389 0.6918749861685528 0.8648052870098396
0.7595162123757241 0.2391418457892084 0.3402576351144293
0.1473261899861980 0.3709222233120330 0.4682213790034302
0.1421840618221771 0.3140746572683427 -0.1121762131537217
1.3389241568069978 0.3988616347426453 0.1635703018210843
-0.2448915061544370 0.7563953018862059 -0.0736150977487566
0.7590706624915531 0.4910146399954628 0.4684780730777085
0.7950571409085634 0.7192143646959017 0.5985905369710599
0.1316279824003455 1.0999687910648197 0.7533188747497124
0.1904139474335156 0.7791943520426338 0.0571106523349340
1.2220229066248534 0.3192108772536086 0.2369051680927172
0.3612775881033622 0.0855989478292645 0.1403208309917672
-0.1361272699805649 0.6820997653177969 0.2354821840318570
0.4087521084198726 0.5912825002582747 0.6358439098196149
0.1239762404674222 0.7546282143520640 -0.2004037475678275
0.3254524437469295 0.5629691201597067 0.3724966107408161
0.4753895829795802 1.0167551557396182 0.7120469261102015
0.2608638376650217 1.0575489302906138 0.5689964057513199
0.1643499778763993 0.9878520821198175 0.2274680280884254
0.5044272836232667 -0.1889898057206633 1.0969173862764161
1.0108484544264800 0.2499932639019371 -0.0323289029244656
1.4604847395188030 -0.1857921072604787 0.3648781664672482
-0.0676389676130162 -0.0295362893506241 0.7871165868504495
0.4846115199200384 0.2254773218591808 0.1655080485768635
0.7546930244801831 0.9283849256193616 0.8541595795735338
0.9706434056979190 1.1154826414004460 0.5267461552592998
-0.0861615702697154 -0.1809840616227028 -0.6553434728259054
0.8442013982186719 -0.0307048052283226 0.1425354846866949
0.6887583721043200 1.0654555145745237 0.2683125737537906
1.0027728188337521 0.5023071178777798 -0.4225836976328659
1.2932985504962016 1.5692646782719462 0.9368592413035413
0.4716460351076925 0.6993549392273799 0.6601847017954563
0.2065050455598290 0.8340729505249687 -0.1549365584796285
0.7134717637166987 0.6306375489985552 0.5979355450208014
0.1305819547597963 1.1628983978276421 0.6489352069792226
0.1272197155625575 0.8779790277321273 0.1016609192978390
1.2490179100185559 0.1997381130828568 0.2661804901290689
1.3538940004316671 0.0865346934520785 0.0162268012094167
-0.1648144254795892 0.6328837747686877 0.3517458960703262
1.3576963330025944 -0.2535471527532498 0.3451642885788545
-0.1512707063199035 0.0447723975378184 0.7370562480777335
0.2082920817694131 0.6238194842808575 0.3627405505637077
0.4818735663404834 0.0797305025898344 0.8149171190132681
0.2714920258235731 0.9437115667773756 0.5398585008814204
0.0598987571605861 1.0109519535694200 0.1622926257298793
0.5118223005328099 -0.2906673876063635 1.0219508170746381
0.9862800303912808 0.1828001523416312 0.0677466130856736
1.0595449212229817 0.5431076873367398 -0.5303300708777712
1.2934388789888798 0.6286357417906868 -0.1682875581053126
0.4618116975337169 0.2958921133995223 0.2670334121905841
0.7539636581184406 0.9360985551615451 -0.0248108921725196
0.9998082474973725 1.2364748213827927 0.5458537302387204
0.0084172701408917 -0.0989295133906621 -0.6906681930981559
0.9033157610523457 -0.1303930279825006 0.1228072425414686
0.6604461112340703 0.9892487041136045 0.1825505778817879
0.7885276375808787 0.6294686108635517 -0.0737926736153585
0.8840546243663174 0.5053739463625377 0.4526376410385395
0.8074749932462770 0.2947711469591280 0.7787234411725377
0.4632367138215856 0.6097289940035490 -0.1145492866143238
0.7775247539743841 0.1357560792893380 0.4055163611357055
0.2117515661833950 0.2832304177268588 0.4122050502626490
0.0768107057290735 0.4027427851525467 -0.0515166562421230
1.2669405505626230 0.4880120983162565 0.2202021018146102
0.2919481531025963 -0.0097036832216508 -0.0729957055081244
0.9840898695695925 0.7046088238612841 -0.1980300785209053
0.5582639462588442 0.7673812911725254 -0.2587733472825737
0.8220678952661906 1.3361683524558097 0.2699860947274584
0.7257118638315225 0.4999486906307656 0.6412374880809832
-0.0159466690459744 0.1935938619023044 -0.7768095097490648
0.9155392077434708 1.0805930191162569 0.4138690591165022
0.7862174758070717 0.1816706702550143 0.6732485622988889
0.6132430910865457 0.6183045290387048 0.2587122784691759
0.5240798045171384 0.0270658373485661 0.5490772798003927
0.6227258931836714 -0.1513468939644967 0.4514026249947363
0.9638867643770986 0.4954513053854325 0.7212510085139069
0.7159100053950270 0.4678155943640417 0.1349439087134111
0.4582333315581760 0.5168500155232567 0.4094860848574138
0.6020128307710225 1.2064430441579375 -0.4506555458643959
0.5521951499401644 0.9590467759911693 0.0741168885795418
1.0781674762106039 0.4954947302196762 0.0441857869962515
1.2877834938552375 0.0081337644237061 1.2888612376304034
1.2732518381606885 -0.3103063836930492 0.0984742851109190
0.5595086990259246 0.3696506726448117 0.6743217671307982
0.1240887034225702 0.6960193789405823 0.4337932939025890
0.5086138696669937 1.2114646205434219 -0.1402693575758740
0.7313300345574206 0.5088192316865796 -0.0848414107423346
0.6392500541546888 0.2452966478859945 0.0290217369836307
0.2906220813433669 0.2834501467738138 -0.1612157326655933
0.9265368908511590 -0.1886857109185944 0.5950530730285820
0.4191322585983637 0.2968514680208339 0.4065358381730697
0.9503223312345728 0.6924078287564821 0.0976010227803059
0.3171226540194806 0.4277726129695098 0.6291827895026040
0.2523597102929802 0.7992029127084535 -0.4251410697001895
1.0542894643082081 0.0098095875712209 -0.1254405527744111
-0.1850276732646079 0.7064002231521372 -0.0809385398102708
0.8146436675316787 0.5091462597700946 0.4152356140927696
0.8203699138320668 0.3369968354028824 0.8455921310438892
0.5350509729728494 0.6295527668603674 0.9102304780657455
0.7193764908855955 0.1838347476185205 0.3819141293957220
0.1910314352006382 0.3094472630165150 0.4823838977521944
0.0687276874475614 0.3407534564140682 -0.0961793949793184
1.2668203814128003 0.4259424135404398 0.1731136054217358
0.4280856307534187 0.6584589779898570 0.6012619513268567
1.1963611411889725 0.7804022094739607 -0.2110274995492418
0.7214250257605557 0.7065604538172952 0.5794991635695482
0.1776849231487917 1.1234852797096138 0.6937893559514705
0.1285406853584958 0.8283735895779946 0.0360212378784548
1.1982000164502744 0.2527276897017764 0.2755163953762200
0.3971884946158640 0.1135585073114126 0.0762033607013268
-0.1677109438487009 0.6976010251448760 0.3070009760429893
1.3843291659064216 -0.1806544740790267 0.3487638347163066
-0.1370877275115541 -0.0294965108434674 0.7526972827056088
0.2742057504147322 0.5976400628879622 0.3238891214955297
0.4681381611246405 1.0080818685930206 0.7875962423618043
0.2988391245755818 1.0128379546679014 0.5215141172374251
0.0979325070909129 0.9559351747734792 0.2036472418484847
0.4871098095650768 -0.2661593993271190 1.0958159235212488
0.9840996652256983 0.1761359392656111 -0.0086227132193279
1.0181722221064600 0.4832974111083591 -0.4993793874483681
1.3336737594231565 0.5733445036683216 0.8701294276086065
0.4805509314794579 0.2981571227457179 0.1930037183242462
0.7146125697156993 0.8998617569525493 0.9145452976881076
0.9916627840023351 1.1683363103812550 0.5804316669886708
-0.0389136332191330 -0.1241670083541440 -0.6326131437048044
0.8956869974284227 -0.0586980011006573 0.0867714766274296
0.7097227556462733 0.9934862114531017 0.2391419679113634
Related articles
Machine-learned force fields, Ionic minimization, Molecular dynamics, Machine learning force field calculations: Basics