STM of graphite: Difference between revisions
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
{{Sur_sci}} | {{Sur_sci}} | ||
[[Category:Examples]] | [[Category:Examples]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:19, 14 November 2019
Overview > Ni 100 surface relaxation > Ni 100 surface DOS > Ni 100 surface bandstructure > Ni 111 surface relaxation > CO on Ni 111 surface > Ni 111 surface high precision > partial DOS of CO on Ni 111 surface > vibrational frequencies of CO on Ni 111 surface > STM of graphite > STM of graphene > collective jumps of a Pt adatom on fcc-Pt (001): Nudged Elastic Band Calculation > List of tutorials
Task
Generation of an STM image of a graphite surface.
Input
POSCAR
C: Graphite Lattice 1.0 +2.4410462393 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 -1.2205231197 +2.1140080551 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +22.0000000000 10 Cartesian +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +3.3070243927 +1.2205231197 +0.7046693517 +3.3070243927 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +6.6140487854 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +6.6140487854 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +9.9210731781 +1.2205231197 +0.7046693517 +9.9210731781 +0.0000000000 +0.0000000000 +13.2280975708 +0.0000000000 +1.4093387034 +13.2280975708
INCAR
general: SYSTEM = Graphite surface slap ENMAX = 400 ISMEAR = 2 ; SIGMA = 0.2 ALGO = Fast
partial charge densities: LPARD = .TRUE. LSEPK = .FALSE. LSEPB = .FALSE. NBMOD = -3 EINT = -0.1 0.1 # DOS: # ISTART = 0 # ICHARG = 2 # LORBIT = 11
KPOINTS
K-Points 0 Monkhorst-Pack 9 9 1 0 0 0
- Only one k point in z direction since we have a surface.
Calculation
- First copy INCAR.DOS to INCAR to get the lm-decomposed DOS.
- Second copy INCAR.par to INCAR and run VASP for the preliminary calculation.
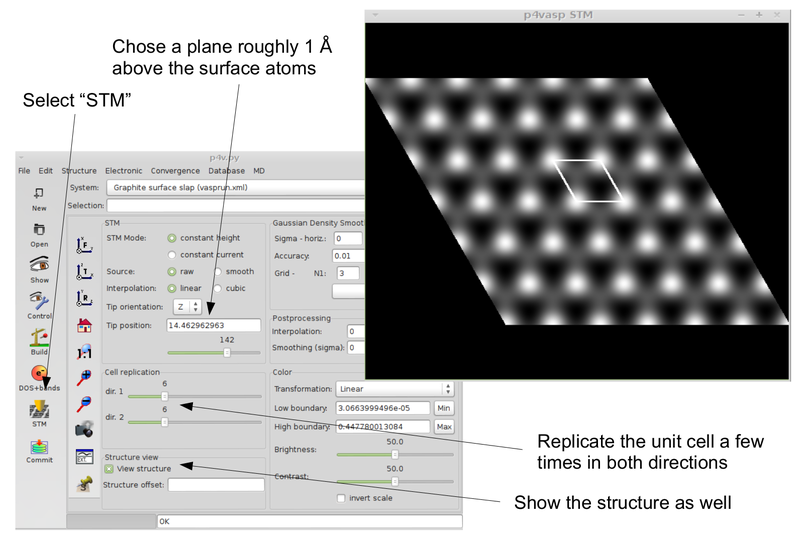
- To get an STM image use p4vasp:
Download
Overview > Ni 100 surface relaxation > Ni 100 surface DOS > Ni 100 surface bandstructure > Ni 111 surface relaxation > CO on Ni 111 surface > Ni 111 surface high precision > partial DOS of CO on Ni 111 surface > vibrational frequencies of CO on Ni 111 surface > STM of graphite > STM of graphene > collective jumps of a Pt adatom on fcc-Pt (001): Nudged Elastic Band Calculation > List of tutorials